HSE Scientist Optimises Solution of Hydrodynamics Problems

Supercomputers are no longer required to calculate fluid flows in multiscale problems.
Roman Gaydukov, Associate Professor at the MIEM HSE School of Applied Mathematics, has modelled the fluid flow around a rotating disk with small surface irregularities. His solution allows for predicting fluid flow behaviour without the need for powerful supercomputers. The results have been published in Russian Journal of Mathematical Physics.
Hydrodynamics studies the motion of fluids and their interaction with solid surfaces. This branch of physics makes it possible to understand and predict the behaviour of fluids and gases under various conditions. In particular, the principles of hydrodynamics are used in electrochemistry for calculating the reactions of galvanisation, such as silver molecules adhering to a metal surface, and oxidation, such as patina formation on copper.
These processes use a disk electrode, which is a flat metal plate that rotates in a fluid. To accurately calculate electrochemical reactions, it is essential to understand how the fluid moves around the electrode and what conditions that need to be maintained. To achieve this, scientists must account for numerous variables, while even minor irregularities on the disk surface can greatly influence fluid flow, leading to complex and unexpected effects.
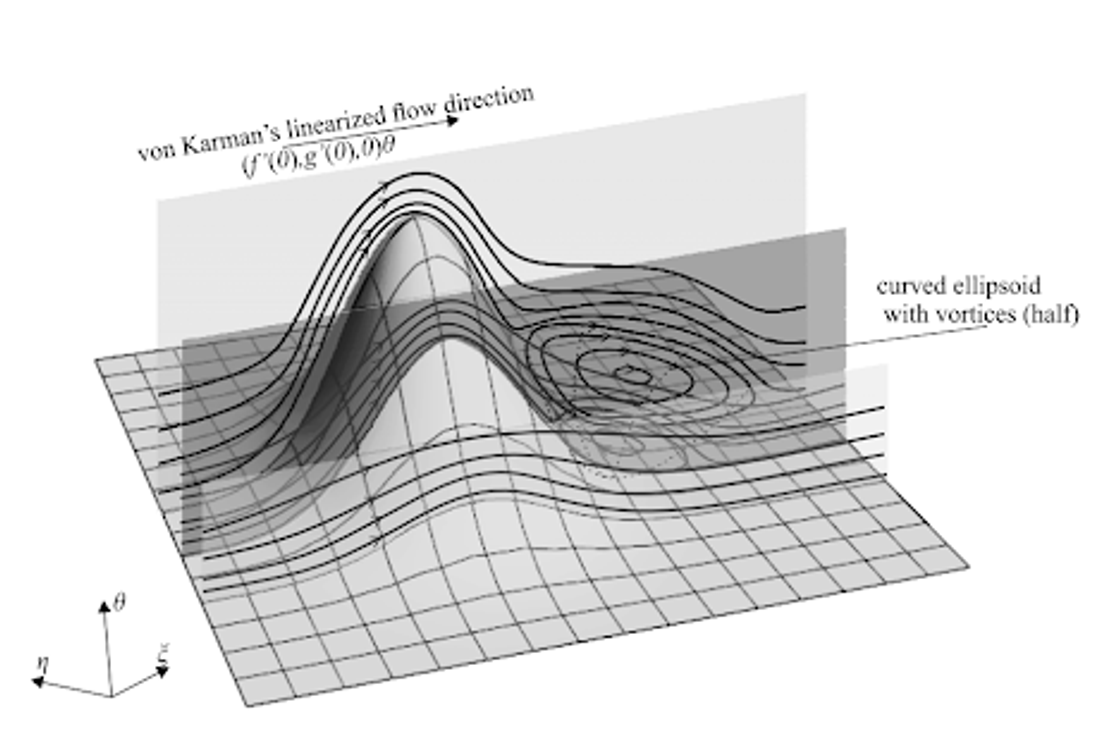
Earlier studies focused solely on symmetrical irregularities, but a scientist at HSE University examined a more complex case. Roman Gaydukov calculated how fluid flow would change with the presence of asymmetrical irregularities on the rotating disk surface.
To do this, he used the method of multideck structures of boundary layers, making it possible to decompose the three-dimensional problem into a series of two-dimensional ones. This method helps solve complex hydrodynamic problems at high Reynolds numbers, where direct modelling is impossible. Although this method has been known since the late 1960s, a rigorous mathematical formulation was only recently developed by the author of the paper together with Professor Vladimir Danilov. The mathematical algorithm of the method can be integrated into any symbolic computation software.

Roman Gaydukov
'Under real conditions, perfectly smooth surfaces do not exist. We have demonstrated how small irregularities on the disk surface affect fluid flow by creating vortex zones and altering the structure of the boundary layer,' explains Roman Gaydukov. 'Our method allows modelling a problem within a few hours, whereas it could take days or even weeks on a supercomputer. This not only saves time but also reduces the cost of computational resources. The method works effectively for large but finite Reynolds numbers.'
The Reynolds number is a dimensionless quantity that describes the relationship between inertial and viscous forces in fluid flow. A large Reynolds number signifies the dominance of inertial forces, which often results in turbulent (chaotic) flows, while a small Reynolds number indicates the dominance of viscous forces, leading to laminar (ordered) flows.
The developed approach can be used to accurately model fluid motion during chemical reactions, with potentially wide applications in industry.
In the future, the scientist plans to extend his research to more complex systems involving interactions between different phases, such as liquid droplets in an air stream or aerosols. This will enable a deeper understanding of the processes in multicomponent and multiphase systems and help improve existing models.
According to Gaydukov, 'Together with my graduate student Nikita Burov, we plan to investigate how the shape of fluid droplets changes as they move through an air flow and how the droplets, as irregularities—including their potential freezing—affect the flow.'
See also:
HSE Psycholinguists Launch Digital Tool to Spot Dyslexia in Children
Specialists from HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain have introduced LexiMetr, a new digital tool for diagnosing dyslexia in primary school students. This is the first standardised application in Russia that enables fast and reliable assessment of children’s reading skills to identify dyslexia or the risk of developing it. The application is available on the RuStore platform and runs on Android tablets.
Physicists Propose New Mechanism to Enhance Superconductivity with 'Quantum Glue'
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that defects in a material can enhance, rather than hinder, superconductivity. This occurs through interaction between defective and cleaner regions, which creates a 'quantum glue'—a uniform component that binds distinct superconducting regions into a single network. Calculations confirm that this mechanism could aid in developing superconductors that operate at higher temperatures. The study has been published in Communications Physics.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
'Even among Geniuses, Luck Plays a Role in Winning a Nobel Prize'
Denis Bodrov studies particle physics and works at one of the four electron–positron colliders in the world. In this interview with the HSE Young Scientists project, he talks about his efforts to go beyond the Standard Model, discusses tau leptons, and shares his affection for Moscow.
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
New Models for Studying Diseases: From Petri Dishes to Organs-on-a-Chip
Biologists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the Kulakov National Medical Research Centre for Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, have used advanced microfluidic technologies to study preeclampsia—one of the most dangerous pregnancy complications, posing serious risks to the life and health of both mother and child. In a paper published in BioChip Journal, the researchers review modern cellular models—including advanced placenta-on-a-chip technologies—that offer deeper insights into the mechanisms of the disorder and support the development of effective treatments.
Using Two Cryptocurrencies Enhances Volatility Forecasting
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have found that Bitcoin price volatility can be effectively predicted using Ethereum, the second-most popular cryptocurrency. Incorporating Ethereum into a predictive model reduces the forecast error to 23%, outperforming neural networks and other complex algorithms. The article has been published in Applied Econometrics.
Administrative Staff Are Crucial to University Efficiency—But Only in Teaching-Oriented Institutions
An international team of researchers, including scholars from HSE University, has analysed how the number of non-academic staff affects a university’s performance. The study found that the outcome depends on the institution’s profile: in research universities, the share of administrative and support staff has no effect on efficiency, whereas in teaching-oriented universities, there is a positive correlation. The findings have been published in Applied Economics.
Physicists at HSE University Reveal How Vortices Behave in Two-Dimensional Turbulence
Researchers from the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the HSE University's Faculty of Physics have discovered how external forces affect the behaviour of turbulent flows. The scientists showed that even a small external torque can stabilise the system and extend the lifetime of large vortices. These findings may improve the accuracy of models of atmospheric and oceanic circulation. The paper has been published in Physics of Fluids.
Solvent Instead of Toxic Reagents: Chemists Develop Environmentally Friendly Method for Synthesising Aniline Derivatives
An international team of researchers, including chemists from HSE University and the A.N. Nesmeyanov Institute of Organoelement Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INEOS RAS), has developed a new method for synthesising aniline derivatives—compounds widely used in the production of medicines, dyes, and electronic materials. Instead of relying on toxic and expensive reagents, they proposed using tetrahydrofuran, which can be derived from renewable raw materials. The reaction was carried out in the presence of readily available cobalt salts and syngas. This approach reduces hazardous waste and simplifies the production process, making it more environmentally friendly. The study has been published in ChemSusChem.